Description
A server room is a dedicated space for housing computer servers and other network equipment, where proper electrical systems are essential for maintaining optimal performance, preventing damage, and ensuring safety. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the electrical aspects of a server room:
1. Power Supply
Main Power Source: A server room relies on a reliable main electrical power supply from the utility grid. Typically, this supply will come through a single-phase or three-phase electrical system, depending on the load.
Backup Power (UPS): Since server rooms house critical infrastructure, uninterrupted power supply (UPS) systems are crucial. The UPS provides temporary power during power outages, allowing servers to remain operational until backup generators are activated. It also protects against power fluctuations, spikes, or surges that could damage the equipment.
Backup Generators: For longer power outages, a diesel or gas-powered backup generator is typically used to ensure the room stays operational for an extended period. The generator should be capable of handling the total load of all the servers, networking equipment, and cooling systems in the room.
2. Power Distribution
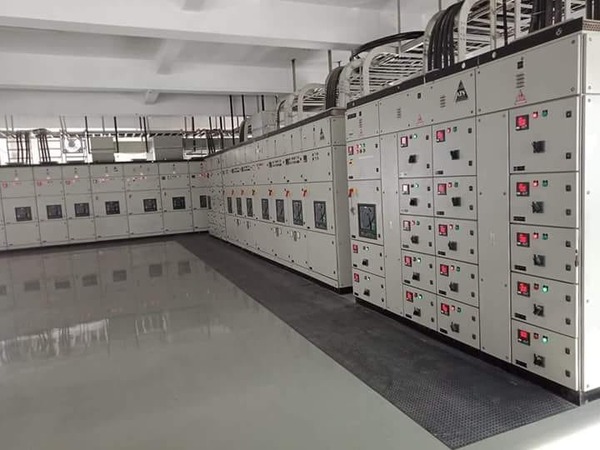
Power Distribution Units (PDUs): PDUs distribute electricity to servers and other equipment within the server room. These devices provide multiple outlets for power connections and are available in different configurations such as basic, metered, and monitored types.
Redundant Power: To minimize downtime, server rooms often implement redundant power systems, meaning each server or critical piece of equipment is connected to two separate PDUs or power circuits. This ensures that if one power source fails, the other can take over without interruption.
Electrical Panel/Distribution Board: The electrical panel or distribution board is responsible for distributing electricity throughout the server room. It connects the UPS, generator, PDUs, and other essential systems to the electrical grid and the backup systems.
3. Voltage and Current Considerations
Voltage Levels: Servers and network devices typically require 120V (in North America) or 230V (in Europe) power. However, high-density data centers or larger server rooms may need higher voltage, often 380V to 415V for three-phase systems.
Current Rating: The electrical wiring, power circuits, and PDUs must be rated to handle the peak current load of the server room’s equipment. Proper sizing ensures the safe distribution of electricity, preventing overheating or overloads.
4. Wiring and Circuit Design
Conduits and Cable Management: Electrical wiring should be neatly organized in conduits or cable trays to minimize the risk of damage, avoid interference with air circulation, and improve the room’s aesthetic and safety.
Separation of Power and Data Cables: To reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) that could affect the performance of data cables, power and data cables are usually kept separate in server rooms. This helps maintain data integrity and reduces potential disturbances.
Circuit Breakers: Circuit breakers protect the electrical circuits from overcurrent conditions, such as short circuits or overloads. They automatically disconnect power to specific circuits when the current exceeds safe limits.
5. Cooling and Ventilation
Electrical Load and Cooling: The electrical load generated by the servers and networking equipment produces significant heat. The power distribution system must be designed to handle the heat produced and ensure proper ventilation and cooling systems.
Cooling Units: Air conditioning or dedicated cooling units, such as Computer Room Air Conditioning (CRAC) systems, are critical in regulating the temperature of the room. The power for cooling units is an integral part of the server room’s electrical infrastructure.
6. Safety Considerations
Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding ensures that electrical currents, including fault currents, are safely directed to the earth, minimizing the risk of electrical shock or equipment damage. Bonding ensures that all conductive parts of the electrical system are connected to the same ground potential.
Surge Protection: Surge protectors or surge suppressors are used to prevent voltage spikes from damaging sensitive equipment. These devices are often installed on the input of the power distribution system.
Fire Prevention: Electrical fires are a significant risk in server rooms, so fire prevention measures, including fire-rated walls, automatic fire suppression systems (e.g., clean agent systems), and smoke detection, should be integrated into the design.
Electrical Inspections and Maintenance: Regular inspections, testing, and maintenance of the electrical systems help detect potential issues before they lead to equipment failure or fires. This includes checking wiring, PDUs, UPS systems, and cooling systems.
7. Electrical Monitoring and Management
Energy Monitoring: Energy monitoring systems track the usage and efficiency of the electrical system. Monitoring tools can detect trends in power consumption, helping to identify areas for optimization and potential overloads.
Smart PDUs: These PDUs are equipped with remote monitoring capabilities, allowing administrators to monitor the electrical load and take necessary actions, such as resetting power or tracking energy consumption, remotely.
Alarm Systems: If any part of the electrical system fails (e.g., UPS or generator), the alarm system will notify the management staff immediately, reducing response time and minimizing downtime.
8. Compliance with Standards
Server room electrical systems should comply with national and international standards for electrical installations. These standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the U.S., International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards, and ISO/IEC 27001 for information security, ensure that safety protocols are followed, and equipment operates reliably.
9. Redundancy and Fault Tolerance
Redundancy is a key feature in any server room electrical design. This includes:
Dual Power Supplies: Each piece of critical equipment should have dual power supplies (from separate PDUs) to ensure continuous operation in case one source fails.
Hot Swappable Components: Electrical components like UPS units, batteries, and PDUs should be hot-swappable to minimize downtime during maintenance or failure.
In conclusion, the electrical setup in a server room is essential for ensuring uninterrupted power, safety, and the efficient operation of the equipment housed there. Careful planning, appropriate backup systems, and regular maintenance are key to minimizing the risk of downtime and ensuring the longevity of the infrastructure.